Define Copula Window
Defining a Copula
After inputs have been selected, or when editing an existing copula, the Define Copula window (Figure 3, below) will be displayed. The Define Copula window allows for the configuration of copulas between two or more input distributions. The window generally has two views (only a few copulas utilize a correlation matrix so this view will only be selected when specific Copula Types are selected):
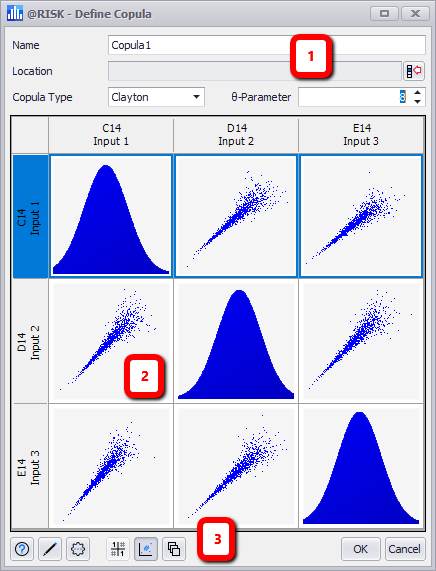
Figure 1 - Define Copula Window
Define Copula Window
The Define Copula window consists of the following primary sections:
- Configuration Panel
- Graphs (alternately, this will display the Instance Editor and for a few copulas, the Correlation Matrix)
- Copula Command Buttons
Copula Configuration Panel
The top panel of the Define Copula window includes options for configuring the appearance of the copula data that will be inserted into the worksheet. The options include:
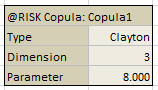
Figure 2 - Copula Data
Unlike correlation matrices, when inserting copula data (Figure 3, right) into an Excel worksheet, there are no options for formatting the data; this is because the copula data written to the worksheet includes only the configurations for the copula and does not include any references to the inputs included.
Working With Copulas
Working with copula configurations is nearly identical to working with correlations; with one exception, all of the commands for Copulas are the same as Correlations, and the functions themselves perform the same operations. The major difference between copulas and correlations are:
- Correlations use a correlation matrix of coefficient values to model the relationship between correlated inputs; copulas do not use coefficients, except for the Gaussian and t copula types.
- Correlations do not have parameters, copulas do (except for the Gaussian type).
- Correlations can use adjustment weights, copulas cannot.
For more information on modifying copulas (adding, editing, replacing, or removing inputs), see Edit Correlations.
For more information on graphs in the Define Copula window, see Correlation Graphs.
For more information on using instances with copulas, see Instance Editor.