Six Sigma Settings
Six Sigma is a set of practices to systematically improve processes by reducing process variation and thereby eliminating defects. For a more detailed explanation of Six Sigma, see the @RISK and SixSigma Guide under the Guides section.
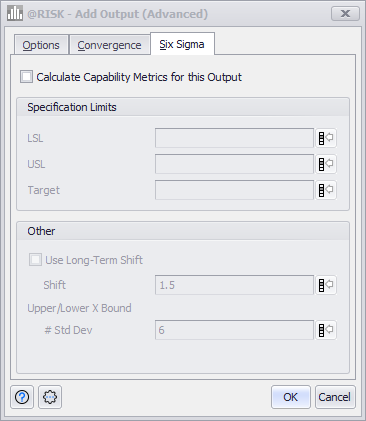
Figure 1 - Six Sigma Settings
Six Sigma settings are turned off by default, and cannot be set for the entire Simulation - they must be set for each Output individually. If the selected Output should use the Six Sigma methodology, those settings are configured in the Six Sigma tab of the Add Output (Advanced) window (Figure 1, right).
When a distribution is configured to useSix Sigma, the @RISK property function RiskSixSigma is added to the function as an optional argument.
Check the 'Calculate Capability Metrics for this Output' box to turn on capability metrics in reports and graphs for the selected Output. The metrics will use the Lower Specification Limit (LSL), Upper Specification Limit (USL) and Target values specified in the Specification Limits section.
Specification Limits
Specification limits provide the target value for the Output distribution, as well as the Lower and Upper limits for the distribution values. Specification Limits are derived from the process requirements, and specify the minimum and maximum acceptable limits of the process. The Lower and Upper limits each fall within 3 Standard Deviations of the mean, for a total of six Standard Deviations.